Nerves: Essential Pathways of the Nervous System
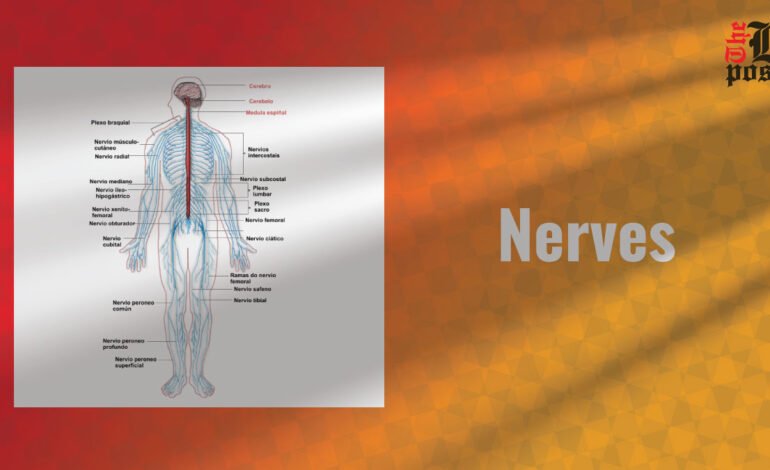
Nerves are the main components of the nervous system, which act as the body’s communication network. They transmit signals between the brain, spinal cord and different parts of the body, enabling important functions such as movement, sensation and reflexes. Understanding is crucial on how the body works and responds to the environment.
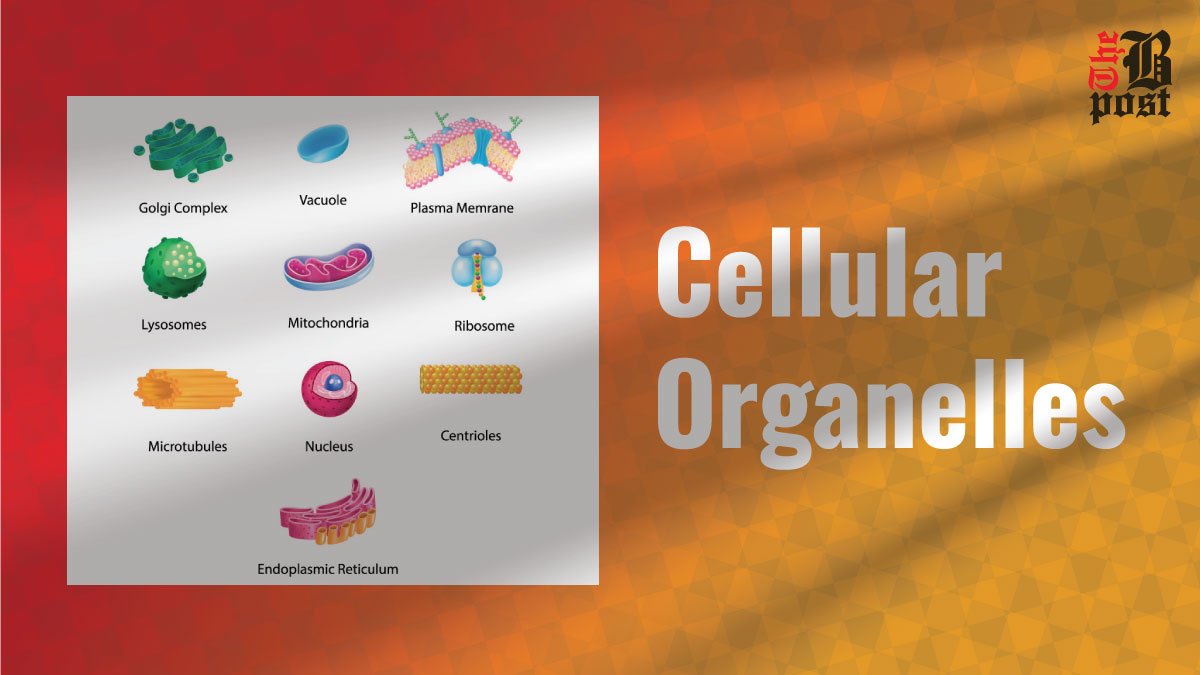
What are Nerves?
Nerves are bundles of axons, the long filamentous parts of nerve cells (neurons) that transmit electrical impulses. These bundles are surrounded by connective tissue and fall into three main types:
Sensory,
motor,
and mixed nerves.
Structure of Nerves
Nerves are designed to protect and facilitate the transmission of signals. Each nerve fiber or axon is surrounded by a myelin sheath, which acts as an insulating layer, speeding up signal transmission. The myelin sheath is produced by glial cells, especially Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system. Axon bundles are further grouped in connective tissues surrounded by perineurium. The entire nerve is surrounded by the epineurium, which provides additional protection and support.
Types of Nerves
Sensory Nerves
These carry sensory information from receptors in the skin, muscles and other organs to the central nervous system. For example, the optic nerve transmits visual information from the eyes to the brain.
Motor Nerves
They transmit commands from the central nervous system to muscles and glands, allowing muscles to contract and glands to secrete. For example, the sciatic nerve controls the muscles of the leg and foot.
Mixed Nerves
These contain both sensory and motor fibers, so they can perform dual functions. Spinal nerves are examples of mixed nerves because they carry both sensory and motor signals.
Functions of Nerves
- Signal transmission: They transmit electrical impulses necessary for communication between the brain, spinal cord and peripheral organs.
- Reflex Functions: Facilitates reflexes, which are automatic responses to stimuli, such as pulling your hand away from a hot surface.
- Movement Coordination: These control voluntary and involuntary muscles, enabling coordinated physical activity.
- Sensory Perception: They allow the body to detect and respond to external and internal stimuli such as touch, temperature and pain.
Nerve Health and Disorders
Maintaining nerve health is very important for overall well-being. Nerve damage can be caused by a number of factors, including injury, infection, diabetes and autoimmune diseases. Symptoms of nerve damage can include pain, numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness. Diseases such as neuropathy, sciatica and carpal tunnel syndrome are common disorders related to the nervous system. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to treat these diseases and prevent new complications.
Conclusion
Nerves are essential to the body’s communication and control systems and play a central role in signal transmission, movement coordination and environmental perception. Understanding their structure and function helps us understand the complexity and efficiency of the human nervous system.
By learning about them, we gain an understanding of the complex workings of our body and the importance of maintaining nerve health for optimal functioning and well-being.