Joints: Types, Functions, and Health
Joints are important structures in our bodies that allow movement and flexibility. They play a vital role in our daily activities, from walking and running to bending and lifting. Understanding the different types, their functions and how to keep them healthy is essential to maintaining an active and pain-free life.
What are joints?
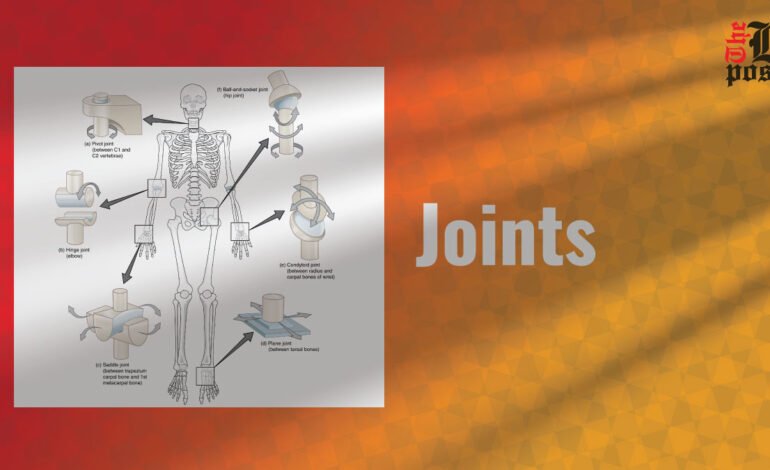
Joints are places where two or more bones meet. They are classified according to their structure and function and allow different types of movement. The human body has over 300 joints, each uniquely designed to perform specific tasks.
Types of joints
- Fibrous joints
Fibrous joint are held together by dense connective tissue that is mainly composed of collagen. These are stationary and are found in places such as the skull where bones fuse to protect the brain. - Cartilaginous joints
These are completely connected by cartilage and allow limited movement. An example is the one between the vertebrae of the spine and the pubic muscle of the pelvis. - Articular joints
Articular joint are the most common and mobile type of joint in the body. They are characterized by a fluid-filled joint capsule that lubricates and cushions the joint. For example shoulder, hip, knee and elbow.
Functions of Joints
- Movement: Joints allow movement by allowing bones to move relative to each other.
- Support: They provide support and stability to bones.
- Protection: Some joints, like those in the skull, protect vital organs.
Common Joint Problems
Joint problems can be caused by a number of reasons, including aging, injury, and disease. Some of the more common joint problems are:
- Arthritis
Arthritis is a group of diseases that cause joint inflammation, resulting in pain, stiffness and swelling. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are the most common types. - Bursitis
Bursitis is inflammation of the small fluid-filled sacs that cushion them. It often affects the shoulders, elbows, hips and knees. - Tendinitis
Tendinitis is inflammation of tendons, the thick cords that connect muscles to bones. It usually occurs on the shoulders, elbows, wrists and heels.
Keeping Your Joints Healthy
- Exercise regularly
Do regular physical activity to strengthen the muscles around your joint, improve flexibility and reduce stiffness. - Maintain a healthy weight
Carrying excess weight puts stress on your joints, especially your knees, hips and lower back. Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce this stress and prevent joint problems. - Eat a balanced diet
Foods rich in calcium, vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids can help keep your bones and joint strong and healthy. Add foods like dairy products, fish and leafy vegetables to your diet. - Avoid Overuse
Avoid repetitive movements that can strain them. Take breaks and use ergonomic tools to minimize joint stress during activity.
Conclusion
Joints are important parts of the human body that facilitate movement, support and protect vital organs. Understanding the different types and their functions helps us understand the complexity of our bodies. By taking steps to maintain joint health through regular exercise, a balanced diet and proper care, we can ensure that they remain healthy and functional throughout our lives.