AI Heart Monitoring Tool Simplifies ECG with Fewer Leads
A game-changing AI solution for heart monitoring has been introduced, cutting down the number of leads needed for precise heart evaluations while keeping the same level of accuracy in cardiac assessments.
Transforming Heart Monitoring with AI
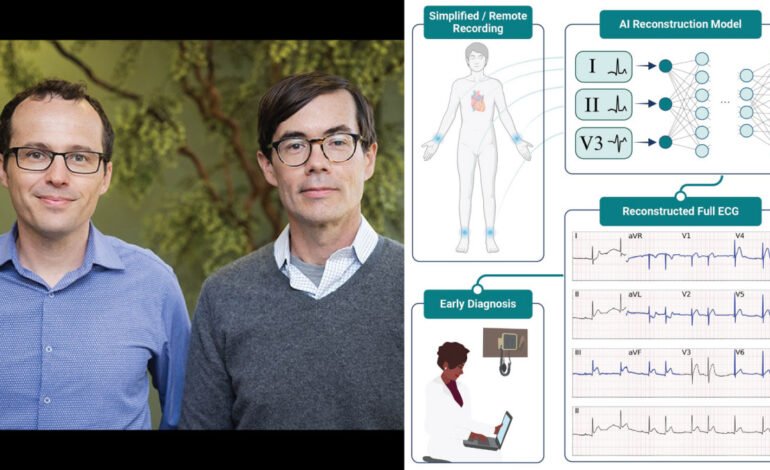
An AI-powered device developed by researchers at Scripps Research, is revolutionizing the cardiac monitoring sector by decreasing the necessity for multiple leads in heart readings. Historically, electrocardiograms (ECGs) have required numerous leads to capture detailed heart activity, which has been inconvenient for patients. However, recent progress has demonstrated that this cutting-edge AI device can achieve the same level of precision with a much smaller number of leads, simplifying the process of monitoring.
The AI program at the heart of this device analyzes heart signals more effectively, making up for the reduced lead count without diminishing diagnostic accuracy. This not only makes the process more comfortable for patients but also streamlines the monitoring procedure, making it more accessible.
Benefits and Use in Medical Devices
The main benefit of this AI device is its capability to simplify heart monitoring without compromising on accuracy. By needing fewer leads, the device simplifies the setup of ECGs, which can be especially advantageous in emergency situations or for remote monitoring. Patients who need frequent heart checks, such as those with heart conditions, will greatly benefit from this technology.
This innovation also has great potential for being integrated into wearable health devices, allowing for continuous heart monitoring in a more discreet and user-friendly way. With the ability to provide accurate readings with fewer leads, it paves the way for more compact heart monitoring solutions, potentially broadening access to cardiac care.
Future Developments in Heart Monitoring Technology
Looking forward, the success of this AI device is expected to drive further advancements in heart monitoring technology. Future developments may include more sophisticated AI algorithms that can diagnose a broader spectrum of heart conditions with minimal equipment. Additionally, as wearable health technology progresses, we can anticipate seeing more devices that incorporate AI-driven heart monitoring features, offering patients real-time information about their heart health.
Moreover, the integration of this technology into telemedicine platforms could transform the way heart conditions are monitored and managed, especially in remote or underserved regions. The combination of AI and telemedicine has the potential to enhance early detection and intervention, leading to improved patient outcomes.
Conclusion
The creation of this new AI device represents a significant advancement in the field of heart monitoring. By reducing the number of leads needed for precise ECGs, the device enhances patient comfort and accessibility while maintaining high diagnostic standards. As this technology continues to evolve, it promises to revolutionize cardiac care, making it more efficient, accessible, and patient-focused.