DNA transcription is a fundamental process in biology that transforms the genetic information stored in DNA into a readable form, mRNA (messenger RNA). The purpose of this article is to provide an educational, accessible and enthusiastic explanation of Deoxyribonucleic acid transcription that is perfect for beginners in biology.
What is DNA transcription?
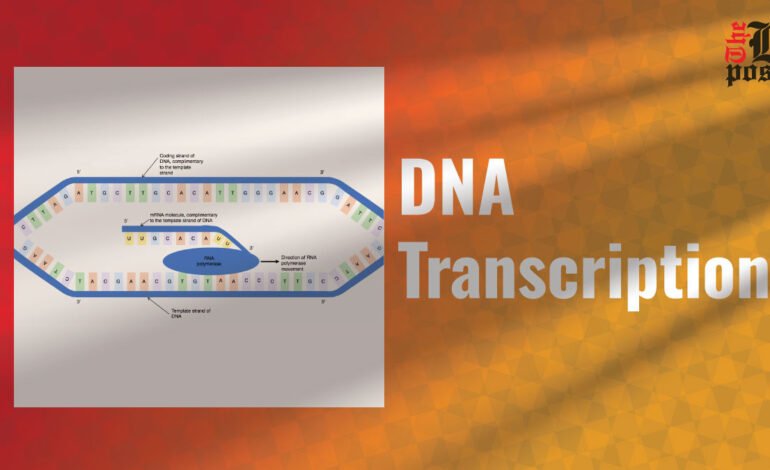
DNA transcription is the process by which the information in a strand of DNA is copied into a new RNA molecule (mRNA). This process is necessary because it allows the genetic code to be read and translated into proteins that are essential for the functioning of all living cells. Without transcription, the cell could not use the information stored in DNA.
Steps of DNA Transcription
Initiation
- Promoter Region: Transcription begins at a specific location on the DNA called the promoter region. Transcription factors and RNA polymerase bind to this region to initiate the process.
- RNA polymerase: This enzyme unwinds the DNA and begins to synthesize the RNA strand by adding complementary RNA nucleotides to the DNA template.
Elongation
- RNA Synthesis: As RNA polymerase moves along the DNA, it continues to add nucleotides to the growing RNA strand. The DNA strand acts as a template and the RNA strand is synthesized in the 5′-3′ direction.
- Transcription bubble: An unfolded region of DNA called a transcription bubble moves with RNA polymerase as it moves along the DNA.
Termination
- End signal: When RNA polymerase reaches an end signal in a DNA sequence, it releases the newly synthesized RNA strand and separates from the DNA.
- RNA processing: In eukaryotes, the original RNA transcript (pre-mRNA) undergoes processing, including 5′-capping, addition of a poly-A tail, and splicing to remove introns, resulting in mature mRNA.
Main Components and Enzymes
- RNA polymerase: The primary enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template.
- Transcription factors: Proteins that help RNA polymerase bind to the promoter region and initiate transcription.
- Promoter region: A specific Deoxyribonucleic acid sequence that initiates transcription.
- Termination signal: A DNA sequence that signals the end of transcription.
Importance of Deoxyribonucleic Acid Transcription
DNA transcription is crucial for several reasons:
- Gene expression: Transcription is the first step in gene expression because it determines which genes are turned on or off in a cell.
- Protein synthesis: mRNA produced during transcription carries the genetic code to ribosomes, where it is converted into proteins.
- Regulation: Transcription is tightly regulated, ensuring that proteins are produced at the right time and in the right amount.
Recent Advances in Understanding DNA Transcription
Recent studies have expanded our understanding of the complexity and regulation of transcription. Advanced techniques in molecular biology have revealed more details about transcription factors, the structure and function of RNA polymerase, and the complex mechanisms that control transcription in different cells and conditions.
Conclusion
Deoxyribonucleic acid transcription is an essential process that converts genetic information into a functional form, enabling the synthesis of proteins necessary for life. By understanding the stages and components of transcription, we gain insight into how cells function and regulate their activities. This knowledge is crucial to the study of biology and has many applications in medicine and biotechnology.